Chapter 4
How does Spread Betting work?
Some traders and investors are a bit reluctant to venture into the world of financial spread betting, simply because it’s a financial product that they’re unfamiliar with.
However, the fact is the spread betting process is one of the simplest types of financial trading there is, much less complex than, for example, the practice of writing options.
We’re moving on to Part II of the guide where we explain what spread betting is and how it works. In this chapter, we’re going to show you exactly how spread betting works, complete with examples of spread bets.
Before we get into that though, let’s briefly recap exactly what spread betting is.
What is spread betting?
Profits are made from betting correctly on which direction the price of a given financial asset will move – up or down. You do not have to predict an exact price the asset will attain – just the direction the market price will move in.
- Learn more, take our free course: Margin Trading Products
Its advantages
This tax-free treatment has made spread betting very popular in the UK, where it is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
First things first – open an account
The first move required to begin spread betting is to open an account with one of the many spread betting brokers. If you’re new to spread betting and want to try out some of your trading strategies before risking real money, you can open a spread betting demo account to practice trade in.
Because spread betting is so highly leveraged, you can start betting with just a small amount of capital. Therefore, many financial spread betting brokers only require a minimal deposit to open an account and begin trading.
You can open a spread betting account at some financial spread betting brokers with as little as £100. However, you should set your expectations of a reasonable rate of return – remember the best traders at hedge funds are probably happy with a 25% annual return on capital.
In short, you’ll probably be in a better position to begin trading if you open your spread betting account with more than just the minimum required initial deposit.
Keep in mind that spread betting is speculation, so you should be sure to fully understand the risks involved and only spread bet with money that you can afford to lose.
- Learn more, take our free course: Understanding Brokers
Learn the trading platform
Spread betting companies offer a variety of spread betting platforms for you to place your bets through. The most common types of betting platforms are as follows:
Web-based trading platforms. With a browser or web-based platform, you trade through a direct internet/web connection, usually through the spread betting company’s website.
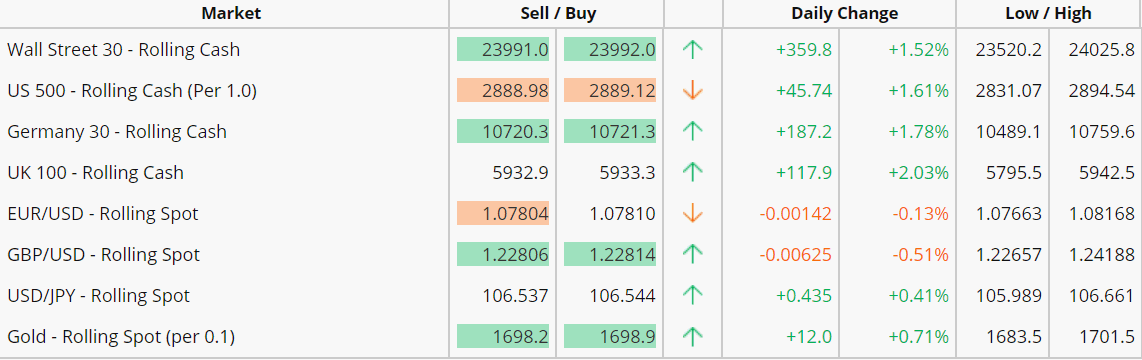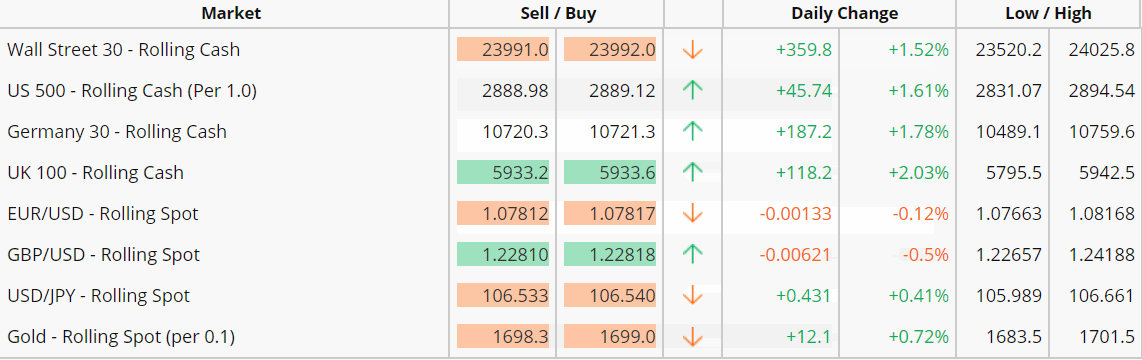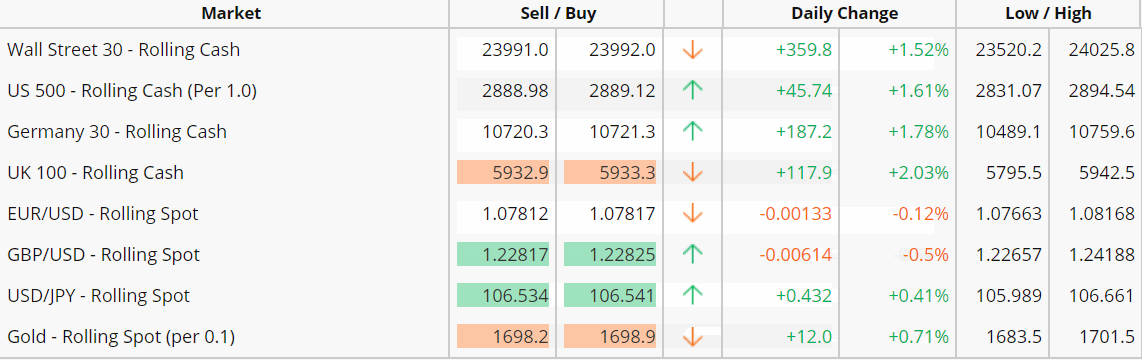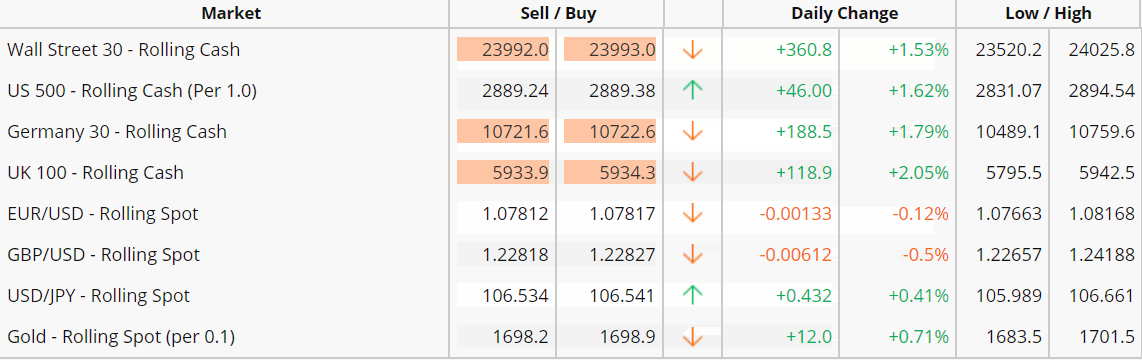
Downloadable trading platforms. These trading platforms are software programs that you download. They frequently offer a number of advanced features beyond what’s available through most web-based trading platforms – such as the ability to access more technical analysis charting tools and templates.
Mobile trading apps. Because more and more traders want the ability to bet “on the go”, using their smartphone, more and more spread betting firms offer a mobile trading app. Although mobile trading apps typically offer a limited number of features, they can easily be used to enter, modify, or close trades, and to access price, market news, and other information.
Read:
It’s very important to familiarise yourself with how your chosen trading platform works – how to enter and exit bets, how to use available research and trading tools, how to modify your bets (e.g. change your stop-loss price), and how to calculate your margin requirement for a bet.
You don’t want to be caught in a rapidly moving market, fumbling around trying to figure out how to enter or exit a bet. To be an effective spread bettor, you need to be able to react quickly to changing market conditions.
You sometimes have literally only seconds to exit a trade with a profit before the market turns sharply against you and hands you a loss.
In addition to providing the means to enter, modify, and exit spread bets, spread betting companies also provide a number of other services to their clients, including the following:
- The latest market news, such as important economic data releases..
- Fundamental market research and technical analysis and commentary from market analysts.
- Live price quotes, along with fully customisable charts and technical indicators.
- Access to your account information, and the ability to make deposits, withdrawals, or transfer funds from one account to another.
Read:
Spread betting – picking your market
There are thousands of possible spread bets available at any moment within the trading day. Spread betting offers a very wide range of financial markets to choose from. Most spread betting brokers offer other types of financial trading as well, such as trading CFDs. Among the most popular markets to spread bet on are:
- Individual company shares, like Amazon and Apple.
- Indices, such as the FTSE 100 or the S&P 500 index.
- Commodities, such as gold, oil, soybeans, wheat and cotton.
- Foreign currency exchange, such as EURUSD, USDJPY and GBPUSD.
- Bonds and interest rates, such and Bobl and Gilts.
- ETFs (exchange-traded funds).
- Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ripple.
Spread betting offers you access to global financial markets – you can spread bet on stocks and other financial assets traded on exchanges in New York, Hong Kong, or Tokyo just as easily as trading on local London trading exchanges.
Since it’s impossible to be an expert on every financial market, or to keep up with the latest information on every traded asset, most spread bettors specialise in betting on just one or two types of financial instrument. You can use your spread betting broker’s research tools to find the markets that you’re most interested in and most comfortable betting on.
You might be particularly good at stock share trading, or you might prefer spread betting forex.
Read:
Spread betting explained – placing your spread bet
For any traded asset, the market price is always quoted showing the spread, which is the difference between the buy price (the ask, or offer, price) and the sell price (the bid price).
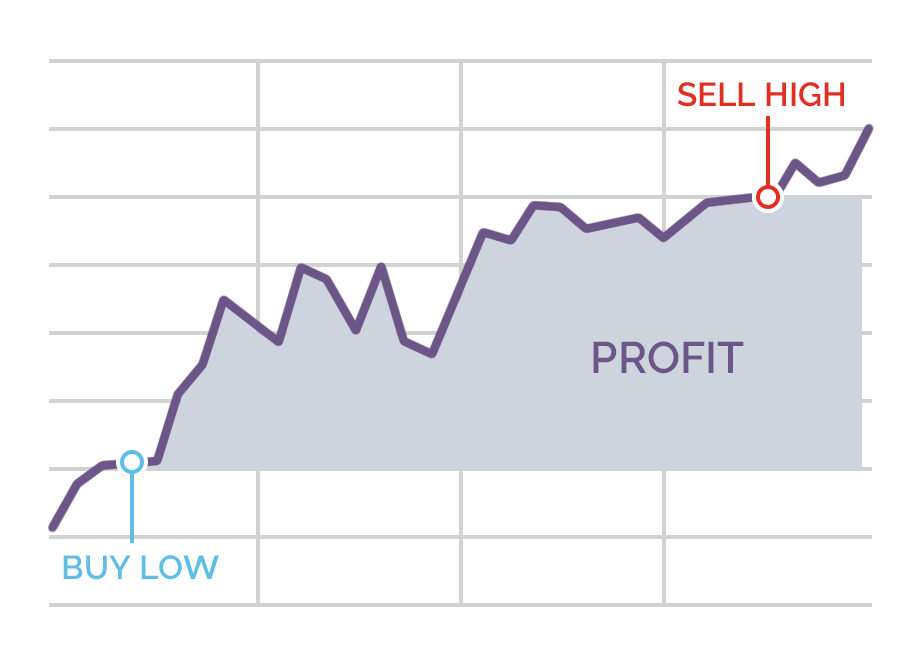
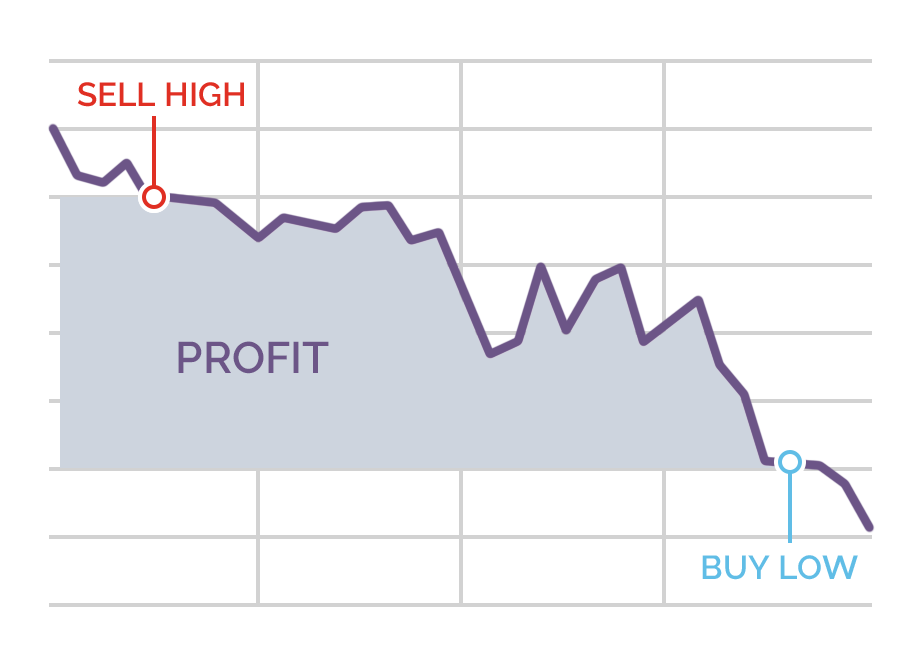
Going long (bullish)
If you are betting on the price of an asset going up, then you buy or ‘go long’ the asset at the buy/ask price, which will always be the highest of the two prices quoted as the spread. You are trying to profit from an increase in price, but you can also lose from a fall in price.
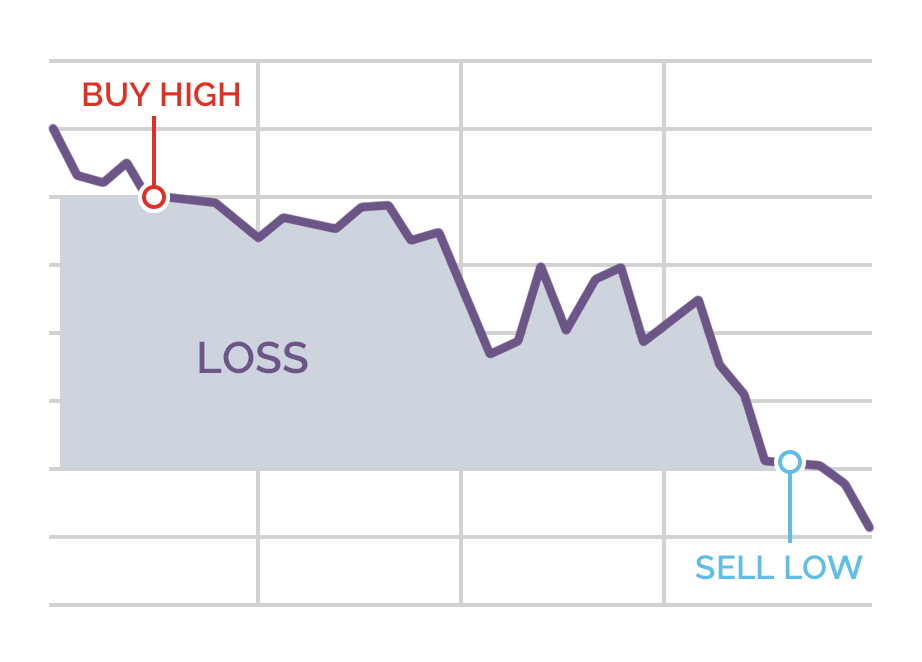
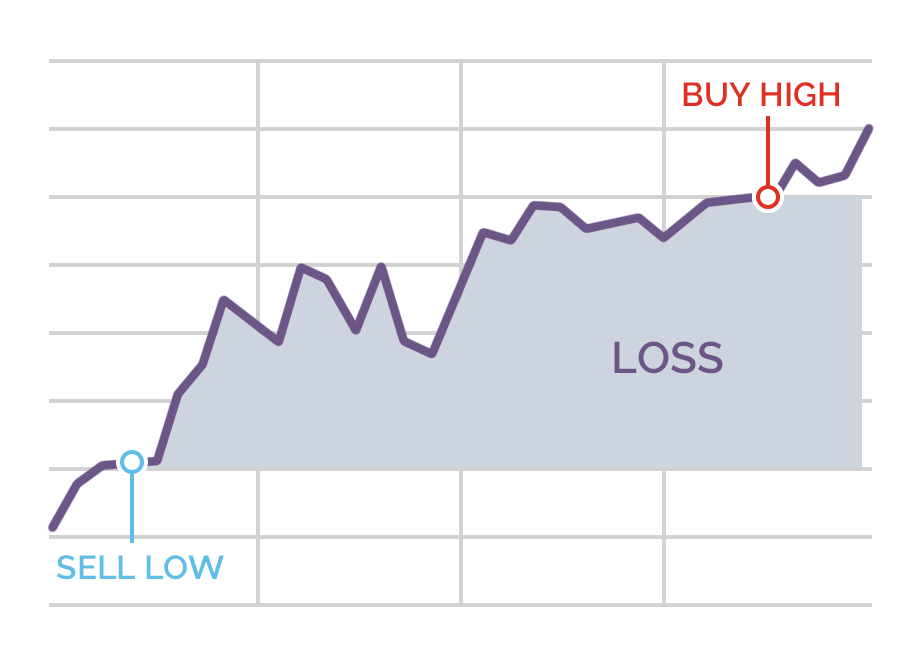
Selling short (bearish)
If you are betting on the price of the asset going down, then you sell short at the sell/bid price, which will always be the lower price quoted in the spread. You are trying to profit from a fall in price, but you can also lose from an increase in price.
Let’s look at an example to see how spread betting works in practice.
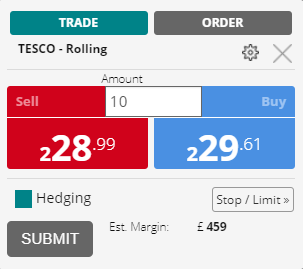
- The current bid/sell price for the stock is 228.99 pence (£2.2899).
- The ask/buy price is 229.61 pence (£2.2961). This means the spread is 0.62 pence (£0.0062)
- You decide to bet £10 per point, a point is one penny. The £10 is your stake amount (see next section, “Stake amount”)
- Since you are selling short, you must sell at the lower price of the spread – the bid/sell price of 228.99 pence.
- You place your spread bet by clicking submit on the deal ticket – sell £10 a point of Tesco. You are required to put up a margin deposit equal to whatever margin percentage the broker requires on the trade, this is 20% of the underlying value of shares bet on – £459 as shown on the deal ticket.
- After about an hour of trading, the stock price has declined by a couple of pence: the bid/selling price is 226.39 pence, and the ask/buying price is 226.81 pence. (Note that the spread has narrowed to 0.42 pence. The spread may narrow or widen during the trading day.) You decide to close out your bet and take your profit.
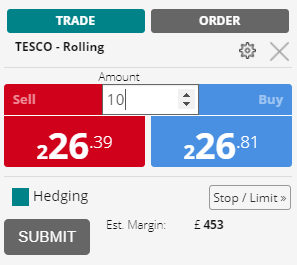
- Since you put the bet on selling the stock short at the bid price, you must now close it out at the ask price of 226.81 – you are effectively buying back £10 per point. Note that the spread is to your disadvantage both opening and closing your bet. You will always have to buy at a higher price in the spread and sell at the lower price in the spread.
- The profit on your bet is £21.80 – the 2.18 point difference between your entry and exit prices (228.99 – 226.81 = 2.18 pence) multiplied by your bet amount of £10 per point.
- With the bet closed, the profit and the margin the broker asked you to put up gets released immediately and is available for you to withdraw or use on another trade.
Stake amount
Whenever you place a spread bet, you have to choose your stake size. Your stake size is basically how much you’re willing to bet per point of price movement of the asset you’re trading. If your stake size is £5, then you make a £5 profit for every point the market moves in your favour.
Likewise, you’d lose £5 for every point the market moves against your position.
Your stake size also determines how much margin you must put up to place your spread bet.
To place your spread bet, you have to put up the required margin percentage (which, of course, varies depending on what financial asset you’re trading and your broker, for the Tesco trade it was 20%) multiplied by the notional value of the underlying asset. The larger your bet, the more margin required for the trade.
Daily-funded and rolling bets
There are two types of spread bets, in terms of how long the bet is good for:
You can control your risk level and set take-profit levels with the use of stop-loss orders and limit orders. Learning to manage your bets well once you have them in place is a key part of learning how to spread bet successfully.
Stop-loss orders explained
You place a stop-loss order at a price level that represents a certain amount of loss, in case the market moves against you. This will limit your potential loss on the bet to an amount you are comfortable with. With a standard stop-loss order, if the market hits your stop price, then your bet will automatically be closed out at the best available market price.
So, for our Tesco example, when going short the stop-loss order is set above the market price – a ten-point stop loss would be set at 238.99 pence. We staked £10 per point, so if the trade moved against us, the stop loss triggered and filled at that level it would be a £100 loss.
This does not guarantee that your order will be filled at the exact price level of your stop-loss, only that it will be filled at the best price available. If the market is moving rapidly or is closed but reopens at a price that then triggers your order, your bet might be closed out at a substantially different price. This fluctuation in order fill price is known as “slippage”.
If you want to be assured of avoiding market slippage, then you can pay a small premium to place a “guaranteed stop-loss order”. With a guaranteed stop-loss, you are guaranteed to have your bet closed at the exact stop-loss price level you specified in your order.
Limit orders explained
You can set a limit order to automatically close out your spread bet if the asset you’re trading reaches a certain level of profitability. In the example above of selling short Tesco, you could have set a limit order to close out your stock spread bet at, for example, 210.00. If the ask price fell to at least that level, your spread bet would automatically be closed out, thus locking in 19.61 points of profits – or in monetary terms £196.10. In our example, we closed the trade out before the limit order level was reached.
If you ever get confused with the terminology, here’s how to remember how limit and stop orders work:
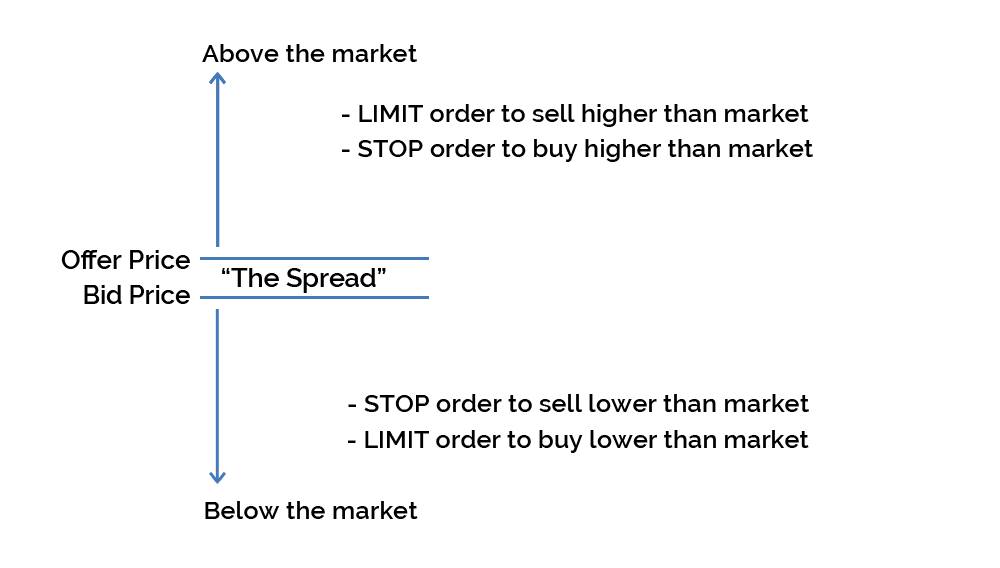
- Learn more, take our free course: How Traders Interact with the Markets
And that’s how spread betting works:
- You open an account with a spread betting broker and fund it.
- You decide what market(s) you want to trade and whether you want to buy or sell.
- You use a trading platform to enter your bet and open your position, modify your position, and close your position.
- You can use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and limit orders to take profits.
- Your profit/loss on any bet is the number of points the market moves, multiplied by your stake size.
The process of spread betting is simple…it’s making sure you bet the right way that’s the challenging part.
Start learning now
Learn the skills needed to trade the markets on our Trading for Beginners course.